*This article was last updated on 03/07/2023
Today, we will crack the code on something essential yet often misunderstood: technical SEO. I know what some of you might think: “Technical SEO? It sounds like geek-speak to me!” But trust me, it’s important.
Like a car engine, once you understand the essential parts and how they work together, the whole thing becomes much less intimidating. And believe me, the technical aspects of your website aren’t less complex than a car engine.
We’ll explore technical SEO, why it matters, and, most importantly, how to get it done right.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the behind-the-scenes elements that help search engines like Google crawl, interpret, and index your website. It’s about making your website accessible, understandable, and friendly for search engines and users.
It’s the base upon which all your other SEO efforts sit. You can spend a fortune in time and money on research and content marketing but will still face problems if your website isn’t technically optimized.
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
Search engines can easily crawl and index your content when your website is technically sound. If they can’t do that, your site’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) will take a hit.
It’s also worth noting that technical SEO is not just about search engines; it’s about users too. Google has clarified that user experience is a significant factor in its ranking algorithm. Users will quickly leave if your site loads slowly or is difficult to navigate.
Technical SEO helps you avoid these pitfalls and ensure your site is user-friendly, which can lead to improved rankings, more traffic, and higher conversion rates.
8 Technical SEO Optimization Best Practices
Technical SEO is not just about ticking off items on a checklist—it’s about understanding how each part contributes to your website’s overall performance and visibility.
Let’s delve into a more detailed breakdown of these best practices, providing you with the “how” and the “why” behind each action.
1. Prioritize Site Speed
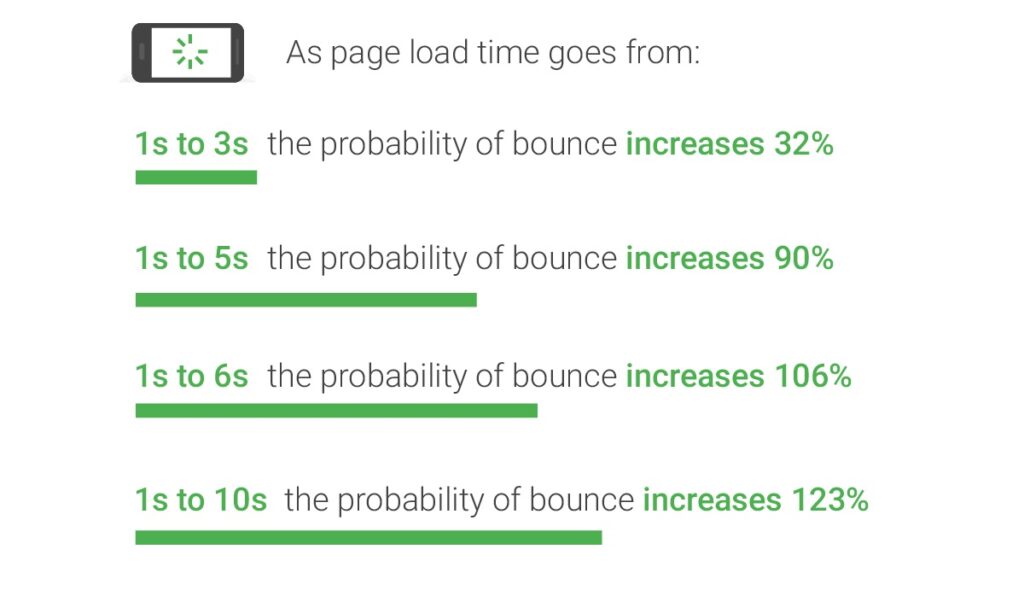
The time it takes your web pages to load significantly impacts user experience and SEO. A slow website can lead to high bounce rates, low dwell time, and decreased conversions—all signals to Google that your site isn’t providing a good user experience.
Image Compression: High-resolution images can take up a lot of bandwidth, causing your site to load slowly. Use compression tools like TinyPNG or JPEG Mini to reduce the size of your images without compromising on quality.
Code Minification: Unnecessary characters like spaces, line breaks, and comments can make your code larger than it needs to be. Minifying your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files removes these characters, reducing the file size and improving load times.
Browser Caching: Enabling browser caching can significantly speed up your site for returning visitors. It allows their browsers to store static files (like your site’s logo) for a certain period, so they don’t have to be downloaded every time the user visits your site.
2. Implement Responsive Design
Mobile devices account for over half of all web traffic. To cater to this audience, your website should adjust to fit the screen size of the device it’s being viewed on—a design approach known as “responsive design.”
This ensures a positive user experience across all devices and is a factor that Google considers in its ranking algorithm. Since 2020 Google has gone with a mobile-first policy for all websites.
3. Use a Secure Sockets Layer Certificate
HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) is the secure version of HTTP. It uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt data transmitted between your website and your users. This provides an additional layer of security and trust.
Trust is essential for websites that handle sensitive information like credit card details or personal data. Google has confirmed that HTTPS is a ranking signal, so it’s worth the investment.
Most websites don’t even need to pay for an SSL. Unless you’re running an online store or otherwise processing sensitive data, you can use Let’s Encrypt. It’s free and widely supported by many web hosts.
4. Create a Clean URL Structure
A well-structured URL should be easily understandable at a glance, both for users and search engines. This involves:
Short and Descriptive URLs: Your URLs should be concise and indicate the page’s content. For example, yourwebsite.com/blog/seo-basics is much more straightforward than yourwebsite.com/12345-6789-221592.
Including Keywords: Where possible, include your target keywords in your URLs. This can provide a slight ranking boost and makes your URLs more informative for users.
Avoiding Special Characters: Special characters can make your URLs clearer and more readable. Stick to alphanumeric characters and hyphens to separate words.
5. Make Use of Schema Markup
Schema markup, or structured data, is a form of microdata that provides search engines with additional information about your content. This can enhance your visibility on SERPs by triggering rich snippets, such as reviews, ratings, or business information.
Schema markup can be implemented using various formats, including JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa. You can rely on some plugins for help with this. The Yoast SEO plugin, for example, helps you implement schema markup automatically.
6. Optimize Your Robots.txt and XML Sitemap
You’ll need to ensure you have these files. They help search engines understand the structure and relationship between your content pieces.
Robots.txt: This file is like a guide for search engines. It tells them which parts of your site they should crawl and which parts they should ignore. Be careful with this file—a mistake could accidentally block search engines from crawling your entire site.
XML Sitemap: Your sitemap is a list of all the essential pages on your site. Submitting it to Google Search Console can help improve your site’s visibility by aiding Google’s crawlers in finding all your content.
You can use Google Search Console to test your robots.txt file and a plugin like Yoast to handle the XML sitemap.
7. Regularly Check for Crawl Errors
Websites are dynamic landscapes. As you add, move, or remove content, issues can crop up that may prevent search engines from crawling and indexing your pages. These could include broken links, 404 errors (when a page that used to exist has been removed), or server issues.
Google Search Console, a free tool from Google, can help you monitor and fix these issues. By addressing these errors promptly, you can ensure that Google’s bots can easily access and index all your content, which is crucial for your visibility in the SERPs.
Moreover, keeping your site error-free also aids in providing a smooth user experience. Nothing is more frustrating for a user than clicking on a link and landing on a non-existent page.
8. Optimize Your On-Page SEO Elements
On-page SEO elements like title tags, meta descriptions, and headers are crucial in helping search engines understand your content. Some areas to pay attention to include;
Title Tags: The title tag of each page should be unique, descriptive, and include the main keyword for that page. This is the first thing users see on the search results page, so make it count. An enticing and relevant title can significantly impact your click-through rates.
Meta Descriptions: These brief snippets describe what your page is about. Although not a direct ranking factor, meta descriptions can significantly impact your click-through rate. They act as ad copy in the SERPs, should be enticing, and include your main keyword.
Headers (H1, H2, etc.): Headers structure your content, making it easier for readers to skim through and for search engines to understand your content.
The H1 is typically the title of your article and should include the main keyword. Subsequent headers (H2, H3, etc.) break your content into digestible sections. Be sure to use them appropriately and include relevant keywords.
Technical SEO vs On-Page SEO vs Off-Page SEO
SEO is a vast field, and it can be helpful to break it down into these three categories: Technical SEO, On-Page SEO, and Off-Page SEO. Each area focuses on different aspects of your website and online presence to improve search engine rankings.
Technical SEO: Refers to all the behind-the-scenes actions you can take to optimize your website for search engines. The goal is to improve your site’s infrastructure, making it easy for search engine bots to crawl and index your site.
It includes actions such as optimizing your site speed, ensuring your site is mobile-friendly, creating an XML sitemap, setting up HTTPS for security, and fixing broken links. It’s about making your website technically sound.
On-Page SEO: Optimizes individual web pages’ content and HTML source code for specific keywords. This includes keyword research, creating high-quality content, optimizing title tags, headers, meta descriptions, and more.
The aim is to create content that is valuable to users and easy for search engines to understand.
Off-Page SEO: Focuses on strategies you can use outside of your website to improve its search engine rankings. Off-page SEO primarily involves building high-quality backlinks to your site from other reputable websites.
This can be achieved through guest blogging, social media marketing, influencer marketing, and brand promotion. These activities signal to search engines that your website is a valuable resource and should rank higher in search results.
Wrapping Up: Technical SEO Essentials and Best Practices
Technical SEO, while less glamorous than content creation and keyword strategy, is the foundation for successful SEO campaigns. Every aspect is pivotal in your site’s interaction with search engines and users.
As we’ve explored, there are many aspects to consider, and the world of technical SEO can be complex. But with a commitment to learning, regular audits, and useful tools, you can ensure your website is technically optimized for search engines and users.
